Build a complete house in just one day andno longer need to maintain it, and most importantly, no utility bills: an ambitious project by American architects. How close is it to reality? We find out in our article ZeroHouse is a project by the architectural firm Specht Harpman, founded in 1995 by Scott Specht and Louise Harpman, then students at the Yale School of Architecture. The firm has offices in New York and Austin, Texas. The concept, called ZeroHouse, is one of the so-called "solar houses." It is designed to be easily transported and quickly erected. The house functions completely autonomously in different climate conditions, providing everything necessary for four adults, which distinguishes it from other prefabricated structures on the market.
Technologies and designs
What was used in construction:
- foundation: cylindrical stainless steel micro-beads with leveling plates;
- carrier system: steel frame made of tubular cold-rolled profile with powder coating;
- enclosing structures: structural insulating panel system (SIPS) with preliminary external lining;
- thermal insulation: the core of the panel made of closed cell polyethylene foam, metallized panel sheath;
- window systems: low-emissivity two-chamber glass, laminated with SentryGlas film, filled with argon;
- external doors: Kevlar shell of the door with a vacuum seal, insulating filler from the airgel;
- Photoelectric batteries: 40 highly efficient solar panels capable of generating a peak of 7,000 watts;
- energy storage: 36 interlocking sealed lead-acid batteries;
- operating voltage: 48 V directly from the batteries and the standard mains voltage is 115 V;
- illumination: concealed illumination by dimmable LED strips, 100 000 hours of continuous use;
- climate control: a two-zone microsplit system with a heat pump;
- water supply: main storage system - four tanks for 2,082 liters of top position for passive pressure, ultraviolet cleaning and reverse osmosis system;
- waste recycling: an auto-composter with a negative pressure ventilation system, compost must be disposed of every 6 months;
- A tubular steel frame can withstandwinds up to 200 kilometers per hour, solar panels are fixed independently and can be separated under extreme wind loads to prevent damage to the rest of the house.
Architectural planning solutions

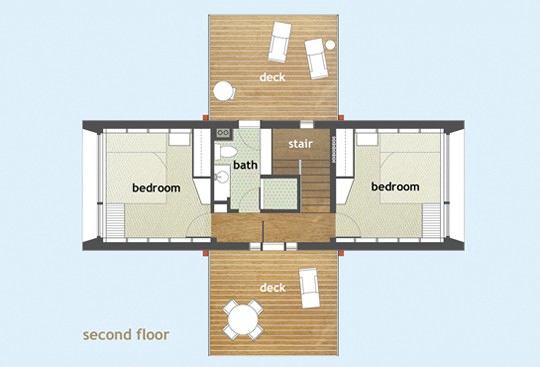
 House area:60 square meters — interior spaces, 23 square meters — exterior terraces. The composition of two perpendicular volumes, the intersection of the first and second floors in the center allows you to place all communications — stairs, risers — in this intersection. Windows the width of the entire wall are one of the characteristic elements of this house, they are used in every room, on all sides of the world. Such a four-sided orientation with large windows is very atypical for energy-efficient solar houses, which is partly compensated by high-tech glazing systems. There is only one bathroom in this house, which is not always convenient for a two-story house. In this project, the first floor is designed as a single space, and the hallway is zoned only conditionally. However, in the case of a colder climate, it will not be difficult to separate it with partitions from both the living room and the kitchen.
House area:60 square meters — interior spaces, 23 square meters — exterior terraces. The composition of two perpendicular volumes, the intersection of the first and second floors in the center allows you to place all communications — stairs, risers — in this intersection. Windows the width of the entire wall are one of the characteristic elements of this house, they are used in every room, on all sides of the world. Such a four-sided orientation with large windows is very atypical for energy-efficient solar houses, which is partly compensated by high-tech glazing systems. There is only one bathroom in this house, which is not always convenient for a two-story house. In this project, the first floor is designed as a single space, and the hallway is zoned only conditionally. However, in the case of a colder climate, it will not be difficult to separate it with partitions from both the living room and the kitchen.
Everything for comfort and relaxation
 A huge sofa that covers the entire living room makes the roomcozy, and the kitchen has enough space for a full-fledged dining area and a bar counter along the window. The view from the windows in this project is a full-fledged element of the interior. The kitchen has a full set of appliances, including an induction hob, a microwave oven and a full-size refrigerator. The living room has a 42-inch LCD TV. The bathroom on the second floor has an unusual solution: it has an exit to a separate terrace with an outdoor shower and sun loungers for sunbathing. The second terrace, shared by two bedrooms, is equipped for breakfasts in the open air.
A huge sofa that covers the entire living room makes the roomcozy, and the kitchen has enough space for a full-fledged dining area and a bar counter along the window. The view from the windows in this project is a full-fledged element of the interior. The kitchen has a full set of appliances, including an induction hob, a microwave oven and a full-size refrigerator. The living room has a 42-inch LCD TV. The bathroom on the second floor has an unusual solution: it has an exit to a separate terrace with an outdoor shower and sun loungers for sunbathing. The second terrace, shared by two bedrooms, is equipped for breakfasts in the open air.
Versatility
ZeroHouse can be built in almost anyOn site: two flatbed trucks deliver the kit to the site and the house can be assembled in less than 24 hours. It can be installed in places unsuitable for conventional construction, including water up to 3 meters deep or slopes up to thirty-five degrees. The design is particularly suitable for use in protected areas and other places where permanent construction is not permitted. The security of the house is also at a high level: all windows are laminated with Sentry-Glass coating to resist penetration. The doors are reinforced on the outside with Kevlar, and integrated locking systems are used throughout. A continuous web monitoring system is also available.
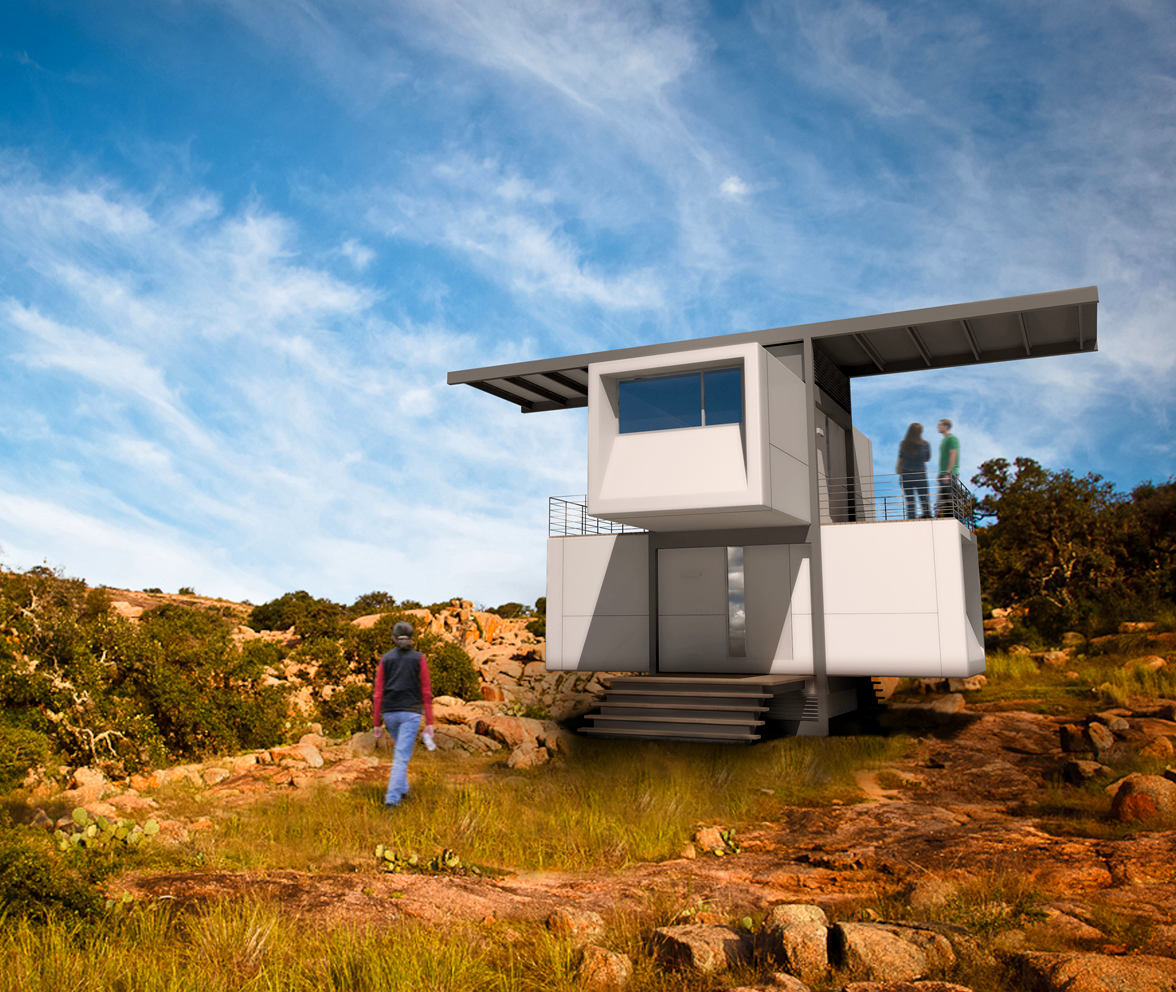

 Our opinion:— The project is sufficiently prepared for Russian conditions, but such architecture is justified only for southern regions. In colder latitudes, magnificent open terraces will sooner or later be glazed… The calculation for energy supply from solar panels will also be justified only in the south. However, the second trump card of this project — quick construction and the status of a temporary structure — is truly universal and is important in any climate and on any terrain.
Our opinion:— The project is sufficiently prepared for Russian conditions, but such architecture is justified only for southern regions. In colder latitudes, magnificent open terraces will sooner or later be glazed… The calculation for energy supply from solar panels will also be justified only in the south. However, the second trump card of this project — quick construction and the status of a temporary structure — is truly universal and is important in any climate and on any terrain.
Energy efficiency
In most cases, calculations show thatZeroHouse is capable of producing electricity in excess of what is required to operate the house. This excess energy can be used for external devices, including charging electric or hybrid vehicles. With ZeroHouse, a life completely free of fossil fuels is possible. Our opinion: - Indeed, autonomy and the absence of operating costs are possible and achievable. However, this requires serious investments at the initial stage: for example, a square meter of an effective solar battery costs 11-12 thousand rubles, and the maximum power on a clear sunny day is about 160 watts per square meter. Thus, the cost of 4.5-5 kilowatt photocells will be about 350 thousand rubles, and this does not include inverters and batteries. For the Russian climate, where the main expense item is heating costs, it is most advisable to strengthen the thermal insulation and arrange a direct solar heating system (glazing on the south side + heat accumulators) or liquid solar collectors. Electricity can be obtained in various ways - photocells, wind generators, even mini-hydroelectric power plants. However, in any case, the initial costs will be quite significant. zerohouse.net



